- News & information
- About
- History
- George V. Voinovich
- George V. Voinovich Collection
- Calendar
- How to Find Us
- News
- Archives
- Photojournalism Fellowship Project
- Photo Essays
- Current Fellow
- Previous Fellows
- Reports and Publications
- Archives
- Students
- Prospective
- Center for Entrepreneurship
- Environmental Studies
- HTC/Voinovich School Scholars
- Master of Public Administration
- Current
- HTC/Voinovich School Scholars
- Center for Entrepreneurship
- Environmental Studies
- Master of Public Administration
- Alumni
- Contact
- School Leadership
- Strategic Partners Alliance
- Ohio University Public Affairs Advisory Committee
- Ohio University Public Affairs Advisory Committee
- Faculty and Fellows
- Faculty
- Visiting Professors
- Voinovich Fellows
- Professional Staff

Basics

 Identifying Patterns and Regularities
Identifying Patterns and Regularities
 Identifying Patterns and Regularities
Identifying Patterns and Regularities
When we observe a particular phenomenon over and over again, we begin to
get a sense of how nature behaves. We start to recognize patterns in
nature. Eventually, we will generalize our experience into a synthesis
that summarizes what we have learned about the way the world works.
Scientists often summarize the results of their observations in a
mathematical form, particularly if they have been making quantitative
measurements. In the case of a falling object
, they might measure
the time it takes an object to fall a certain distance, rather than just
noticing that the object falls.
First step:
Collect data in form of a table.| Time of Fall (seconds) | Distance of Fall (meters) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 45 |
| 4 | 80 |
| 5 | 125 |
Here the time is measured in seconds
and the distance in meters
.
Those quantities are fundamental units The fundamental units are ( SI-Units )
| time | second | s |
|---|---|---|
|
length
|
meter | m |
|
mass
|
kilo gram | kg |
|
temperature
|
Kelvin | K |
Second step:
These data could also be presented in the form of a graph, in which distance is placed against time: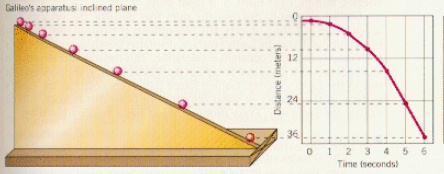
Third step: |
|---|
| After preparing tables and graphs of their data. Scientists would notice that the larger something falls, the further it travels. If an object falls for twice as long as another, it will travel four times as far; if it falls three times larger, it will travel nine times as far, and so on. This statement can be summarized in these ways: |
 In words
: In words
: |
| The distance traveled is proportional to the square of the time of travel. |
 In the form of an
equation
: In the form of an
equation
:
 In symbolic form
: In symbolic form
:Mathematics is a concise language that allows scientists to communicate their results to make very precise predictions, but anything that can be said in an equation can also be said (allied in a less concise way) in a plain English sentence. When encountering equations, you should always ask `What English sentence does this equation represent?'. This nature will keep the mathematics from obscuring the simple ideas that lie behind most equations.
Aug 26 14:27:03 EDT 2019 |
Contact Information:
(740) 593–9381 | Building 21, The Ridges
Ohio University Contact Information:
Ohio University | Athens OH 45701 | 740.593.1000 ADA Compliance | © 2018 Ohio University . All rights reserved.
