- News & information
- About
- History
- George V. Voinovich
- George V. Voinovich Collection
- Calendar
- How to Find Us
- News
- Archives
- Photojournalism Fellowship Project
- Photo Essays
- Current Fellow
- Previous Fellows
- Reports and Publications
- Archives
- Students
- Prospective
- Center for Entrepreneurship
- Environmental Studies
- HTC/Voinovich School Scholars
- Master of Public Administration
- Current
- HTC/Voinovich School Scholars
- Center for Entrepreneurship
- Environmental Studies
- Master of Public Administration
- Alumni
- Contact
- School Leadership
- Strategic Partners Alliance
- Ohio University Public Affairs Advisory Committee
- Ohio University Public Affairs Advisory Committee
- Faculty and Fellows
- Faculty
- Visiting Professors
- Voinovich Fellows
- Professional Staff

Review: Geometrical
Optics
Review: Geometrical
Optics

- Optics terminology
- A `ray' is a beam of light (usually shown as an arrow)
- The `incident' ray shows where the light originated
- A ray can be reflected or refracted from a surface
- The angle of any ray is measured from the perpendicular ( normal ) of the surface to the ray of the reflected light.
- Reflection
- The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection
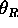 is equal to the angle of incidence
is equal to the angle of incidence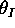 (
(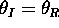 ).
). - What is meant by `diffuse' reflection?
- How does `ray-tracing' locate the virtual image for a mirror?
- What are convex and concave mirrors? What are the image sizes for various shapes of mirrors? What shape magnifies?
- The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection
- Refraction
- What is the refraction condition? (What is Snell's Law?)
- How is the index of refraction defined?
- What is the meaning ofand
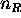 in Snell's Law?
in Snell's Law? - Under what conditions will total internal reflection occur?
- What is a light pipe?
- Lenses
- What are the shapes for a converging lens and a diverging lens?
- How are the images for converging and diverging lenses? Can you construct an image via ray tracing?
- What is the focal length of a lens or mirror, what is the focal point?
- What happens to the light rays at the focal point for a converging lens?
- How is the power of a lens measured?
- What is a retroreflector?
 Ch. Elster
Ch. ElsterAug 26 14:27:03 EDT 2019
Contact Information:
(740) 593–9381 | Building 21, The Ridges
Ohio University Contact Information:
Ohio University | Athens OH 45701 | 740.593.1000 ADA Compliance | © 2018 Ohio University . All rights reserved.
