
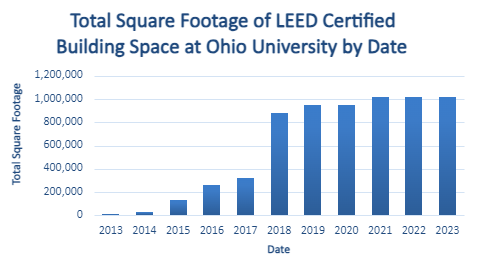
Recognizing that the state and quality of campus buildings can have a significant effect on energy use, waste production, human heath, productivity and tuition prices, Ohio University is committed to maintaining and operating buildings in a way that promotes health, energy efficiency and reduction of waste (see OHIO Green Building Standards ). The Office of Sustainability participates in and supports initiatives that promote best practices in building construction and maintenance. The Athens Campus has more than 1 million square feed of LEED -certified buildings, including Walter International Education Center, Nelson Court Dining Hall, Schoonover Center for Communication Phase I, Bush Hall, Grover Center Expansion, Tupper Hall, Jefferson Hall, Sook Academic Center and the Chemistry Building.
The Sustainability Project Laboratory is a database of sustainability-related project proposals. This resource hosts projects and project ideas that can be adopted by faculty, staff, and students for course projects, capstone or senior projects, theses, and more!
To find buildings related projects just type "buildings" into the search bar at the top of the Project Database on the Sustainability Project Laboratory website.
The Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education (AASHE) is currently revising its Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System (STARS), which Ohio University uses to measure its sustainability efforts. View a Draft of the Proposed Updates
Ohio University Sustainability Plans
Moving Forward: 2021-2026 Sustainability & Climate Action Plan Goal #1
Goal 1: Reduce building impacts by using best practices in construction or divestment (including private partnership, demolition, or sell), by increasing the percentage of FY12 GSF to be low impact from 10.4% to 40%.
Potential Strategies
-
Reduce overall gross square footage (GSF) per student
-
Create and implement Ohio University Low Impact Building Standards for construction, renovation and demolition projects
-
“Low impact” will be defined in more detail in the proposed OHIO Low Impact Building Standards, and depends on building type and usage.
-
-
Support curriculum related to low impact buildings
Benefits of Goal #1
- Reduced operating expense
- Reduced emissions
- Improved occupant comfort and productivity
- Educational and reputational benefits
Costs of Goal #1
- Capital expenses
- Maintenance costs
Moving Forward: 2021-2026 Sustainability & Climate Action Plan Goal #2
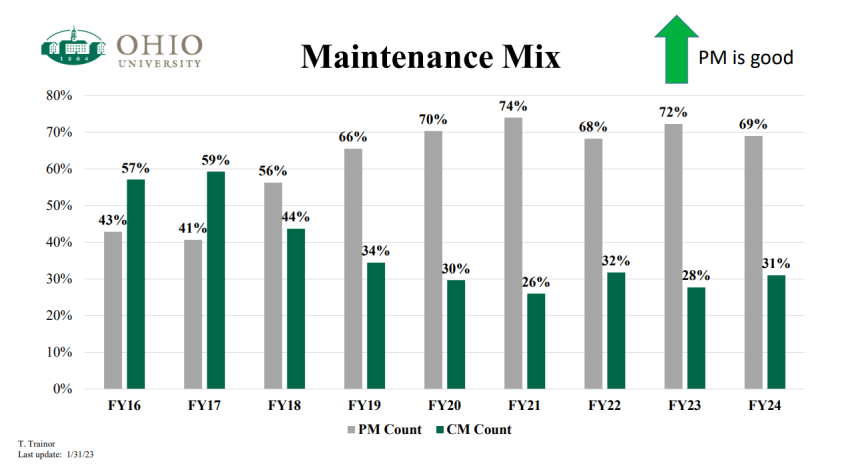
Goal 2: Maintain & operate existing buildings to reduce impacts
- Reduce percentage of hours spent doing corrective maintenance from 83% to 20%
- Increase percentage of hours spent doing preventative maintenance from 17% to 80%
- Increase square footage of setbacks or reduced HVAC schedules from 0 square feet to 1 million square feet
Potential Strategies
-
Expand and institutionalize an OHIO Sustainable Building Operations & Maintenance Program
-
Reduce building resources usage through strategic planning & setback3 utilization
-
Increase OHIO communication & education on reducing building impacts; consider building competitions
Benefits of Goal #2
- Reduced emissions
- Reduced operation costs
- Improved occupant comfort and productivity
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Educational and reputational benefits
Costs of Goal #2
- Increased staff training time
2011-2021 Sustainability & Climate Action Plan
-
Benchmark 4: LEED certify new buildings and major renovations on all campuses. Until 2019, target met: 13 new construction or renovation projects exceeding costs of $2 million were built to LEED Silver standards for 13 building projects.
-
Benchmark 12: Evaluate LEED EBOM of existing facilities. Target met: Tupper evaluated for LEED EBOM in 2018 and ARC in 2019; Cutler partially evaluated in 2012.
Buildings Graphics
AASHE STARS compares programs across the nation in many different categories. Ohio University reports above the national average in buildings.
At Ohio University, buildings produce 65% of our Athens campus emissions. The 76,187 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emitted by our buildings each year is equal to 189,046,628 miles driven by an average passenger vehicle (US EPA). Buildings are the largest producer of carbon emissions, as they blanket many of the sub-categories, such as water and energy . Transportation is also a large contributor, which accounts for just over a quarter of the emissions, which is followed by waste .
Data
Initiatives
2022 Initiatives
| Infrastructure Hub Supported Initiatives | SCAP Alignment |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Audit Treasure Hunt: With funding from the Student Success team, students in ME 4930 Special Investigations: Building Energy Treasure Hunt were given an opportunity to gain hands-on experience on the process of performing an energy audit in Shively Hall |
Reduce campus and building energy intensity; Increase faculty, student, and community engagement across hub themes. |
| 2022 Buildings Seminar: The Infrastructure Hub hosted a seminar on the topics of the experiential learning opportunity provided by the Energy Audit Treasure Hunt and solar farming in partnership with Solar Power & Light. A recording of this seminar can be viewed on the Office of Sustainability Facebook page or on the Energy theme webpage. |
Increase faculty, student, and community engagement across hub themes. |
| Updating Building Standards: The Office of Sustainability is partnering with Design & Construction and Facilities Management staff to update OHIO’s sustainability building standards. The University will be moving to OHIO-specific Green Building standards for all building projects in 2023, replacing former requirements for LEED Silver Certified building construction and renovation for projects over $2 million. |
Reduce building impacts by using best practices in construction, renovation and demolition; Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts; Decrease reliance on fossil fuel energy |
2021 Initiatives
| Sustainable Infrastructure Hub Supported Initiatives | SCAP Alignment |
|---|---|
| Sustainability Project Laboratory: Website of sustainability projects developed for curricular purposes |
Increase faculty, student, and community engagement across all hub themes. |
| Triple Bottom Line Cost Benefit Analysis (TBL CBA) Tool
:
Framework for assessing sustainability impacts. |
Communication and decision-making tool for use in all hub themes. |
| Green roof: Installation on Schoonover Center. |
Reduce impacts from storm water; Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts |
| Sustainable Infrastructure Hub Related Initiatives | SCAP Alignment |
|---|---|
| Design & Construction Infrastructure Design: (D&C) Best practices for D&C project managers |
Reduce building impacts by using best practices in construction, renovation and demolition |
| Regional campus infrastructure: (FMS for RHE) Sustainable initiatives at regional campuses |
Reduce building impacts by using best practices in construction, renovation and demolition |
| Steam system annual shut down: (Maintenance & Operations) Corrective & preventative maintenance best practices |
Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts; Decrease reliance on fossil fuel energy |
| Metering & controls projects: (Maintenance & Operations) Targeting high priority meters and controls |
Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts; Decrease reliance on fossil fuel energy |
| Energy dashboard: (Energy Management) Development of dashboard for energy management |
Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts; Decrease reliance on fossil fuel energy |
| Design & Construction, Surplus, Habitat and ReUse: Partnership with local non-profits to reuse building materials. |
Increase diversion from landfill to reuse, recycling and composting |
| LEED certification of new construction & renovation: Green building standards. |
Maintain and operate existing buildings to reduce impacts; Decrease reliance on fossil fuel energy |
LEED-Certified Buildings at Ohio University
The University's Design & Construction Standards mandate that all new construction or renovations exceeding costs of $2 million must be built to LEED Silver standards.
Currently, there are over one million square feet of LEED-certified buildings on OHIO campuses.
- The Athens campus has 702,046 combined square feet of Silver-certified buildings, including Walter International Education Center, Nelson Court Dining Hall, Schoonover Center for Communication Phase I, Bush Hall, Grover Center Expansion, Tupper Hall, Jefferson Hall and Sook Academic Center.
- Schoonover Center for Communication Phase II, Boyd Dining and Campus Market, Patton Hall and Ellis Hall on the Athens campus contribute 232,085 square feet of Gold-certified square footage.
- The Chillicothe campus is also on the map with the Tech Studies Addition, contributing 14,000 square feet in the Certified category.
Additional information about our LEED-certified buildings is provided below.
15 Park Place
15 Park Place, or the Walter International Education Center , is the home of the Office of Global Opportunities and International Student and Faculty Services. It was the first LEED certified building (12130 sq ft, LEED Silver) at Ohio University.
Scripps
The Scripps College of Communications completed two building projects, Scripps Phase I and Scripps Phase II.
Scripps Phase I was a substantial renovation of Schoonover Center. Scripps Phase I is a 110290 sq ft LEED Silver certified project.
Scripps Phase II was a smaller renovation of Schoonover Center (34950 sq ft), and it was awarded LEED Gold certification.
Patton Hall
Patton Hall is the first full building on campus to earn Gold status. "Patton Hall’s $32.8 million renovation, completed in January 2017, offers students a true 21st-century learning experience. The College’s green-friendly renovation can be felt throughout the building and is summarized on its LEED Wall, which is housed on the third floor. The wall contains various icons and blurbs, as well as an interactive monitor that allows visitors to learn more about the building’s environmentally friendly features, including OHIO’s first green roof, which uses rainfall to conserve water and sustain plant life." (from OHIO News )

Tupper Hall
Tupper Hall is a 38,599 square foot LEED Silver certified renovation, completed in 2015 by local architectural firm BDT. The renovation included a new roof, thermally-efficient aluminum-clad wood windows, and preserved the daylighting features of the original building.
Housing Phase I
Housing Phase I , which includes Tanaka, Luchs, Carr and Sowle residence halls, is a certified LEED Silver project.
Chubb Hall Student LEED Evaluation
FY13 Student Report on Chubb Hall By Rich Wilson
LEED Lab at Ohio University
In 2019, Ohio University became the 31st institution world-wide to offer a US Green Building Council (USGBC) Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Lab course. The Civil Engineering LEED Lab course, CE4540/5540: Sustainable Construction, teaches students to evaluate the operations and maintenance of an existing building on campus using the LEED rating system. A pilot LEED Lab course was taught in the spring of 2018, and a registered LEED Lab course was taught in spring of 2019 and 2020.
A paper will be presented at the June 2020 American Society for Engineering Education annual conference about Ohio University's 2019 LEED Lab course.
Green Cleaning Policy
OHIO's Green Cleaning Policy . Ohio University cleans its buildings according to a Green Cleaning Policy, with the exception of food preparation facilities, which are governed by USDA cleaning requirements, and athletic facilities, which are governed by NCAA cleaning requirements.
Experts and Stakeholders on Sustainable Buildings
Ohio University Experts on Sustainable Buildings
| Name | Contact | Position and Research Interests |
|---|---|---|
|
Cody Petit
|
petittc@ohio.edu | Sustainable Infrastructure Hub Coordinator and Assistant Professor in Mechanical Engineering |
|
Sam Crowl
|
crowls1@ohio.edu | Director of Sustainability |
|
Jesús Pagán
|
paganj@ohio.edu
|
Associate Professor of Engineering Technology & Management |
|
Krista Nutter
|
nutterk@ohio.edu | Instructor of Art Sustainable building design |
|
Mohammed Khurrum Bhutta
|
bhutta@ohio.edu | Professor of Management Sustainable manufacturing |
|
Nichole Campbell
|
ncampbell@ohio.edu | Assistant Professor in the School of Art & Design Sustainable design |
|
Jason Farmer
|
farmer@ohio.edu | Design and Construction Project Manager Sustainability in athletics |
|
Jason Trembley
|
trembly@ohio.edu | Professor of Mechanical Engineering Sustainable building materials |
|
Elaine Goetz
|
goetze@ohio.edu | Director of Energy Management & AVP Facilities Administration |
Other Stakeholders & Experts on Sustainable Buildings
| Name | Contact | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
U.S. Green Building Council
|
https://www.usgbc.org/contactus | A group of professionals who work to promote green buildings in the state of Ohio |
|
Hocking-Athens-Perry County Community Action
|
https://hapcap.org/contact/ | A Community Action Agency with programs in Fair Housing, Home Repair, Development, Weatherization, and others |

